-
Written by Christopher Van Mossevelde
Head of Content at Funnel, Chris has 20+ years of experience in marketing and communications.
Generative AI is no longer a side project for curious marketers. It’s reshaping how marketing professionals work, from testing ad variations to pulling insights from messy customer feedback. A process that once required a copywriter, a designer and a week of back-and-forth can now be tested before lunch.
Adoption is still early. The Spring 2024 CMO Survey found that gen AI is used in just 7% of marketing activities. But usage is rising fast. By mid-2025, many marketers report that generative AI is becoming embedded in their daily workflows. Those who wait much longer risk falling behind.
The real advantage isn’t just speed. It’s the ability to test more ideas without overspending. Teams can compare five versions of a call to action across platforms and quickly shift spend toward the ones that lift CTR or lower CPA.
But generative AI only works when it’s powered by reliable data. Models built on scattered inputs tend to amplify noise instead of insight. Funnel helps solve that by bringing all marketing data together, keeping it consistent and analysis-ready before anything is created, tested or scaled — turning experimentation into measurable performance.
What is generative AI in marketing?
Generative artificial intelligence (AI) refers to a class of deep learning models that produce content, code, design and data analysis. These models rely on neural networks, which pass data through layers of connected nodes. As they train, they learn patterns in language, visuals and audio by analyzing large datasets. Over time, they can generate outputs that match a given prompt with surprising accuracy.
How gen AI works:
- Predicts the most probable next word, pixel or sound
- Trains on data at a massive scale to learn tone, structure and style
- Adjusts to brand inputs like past campaigns, target audiences or product data
What sets generative AI apart is its ability to produce original content that fits a specific format. In marketing, that could mean five versions of a product headline, three versions of a video script or ten ad visuals that reflect the same core offer.
Not all AI in marketing is generative. Tools like Google Performance Max or Meta Advantage+ use AI to optimize targeting and bidding, but they don’t create new content. Generative AI, by contrast, produces copy, visuals and video that can be tested and iterated fast.
Why it matters for performance marketers and content marketing: AI isn’t replacing strategy; it’s amplifying testing velocity and creative capacity. Instead of picking one idea and hoping it lands, marketers can test variations across platforms and see what users respond to. If one image improves CTR by 12% or one line of copy drops CPA by a few dollars, those small wins add up. The value is not in volume. It's in finding the version that actually moves numbers.
How generative AI tools generate outputs marketers can use
Generative AI tools rely on two types of data: structured and unstructured.
Structured data includes campaign performance metrics like CTR, ROAS, purchases and audience segments. This information helps AI tools understand what’s working in current or past marketing campaigns.
Unstructured data includes things like product reviews, chat transcripts, social media posts and customer service emails. These inputs shape tone, language and visual choices that feel natural to real users.
Both data types play specific roles. Structured data improves targeting. Unstructured data helps generate creative assets that connect with audiences.
Marketers still guide the output: It’s worth noting that gen AI tools don’t determine the output on their own. It’s humans that set parameters around tone, length, message type and brand guidelines. Prompts created by marketers might include product details, campaign goals or customer personas. The advanced machine learning models use these to produce ad copy, product descriptions, chatbot replies or social media posts that feel specific, not generic.
The quality of the output depends on the quality of the input. First-party data from systems like a CRM or CDP helps generative models reflect real customer behavior instead of broad internet trends.
That said, marketers need to handle this carefully. Sensitive or personally identifiable information should never be shared with public AI tools. Instead, teams can use anonymized or aggregated data, or work within secure, enterprise-grade environments that comply with privacy and governance standards.
For marketers, the real value comes after creation — in understanding which AI-generated ideas actually perform. That’s where Funnel adds value. Funnel’s conversational analytics and measurement tools help teams analyze results, compare creative variations and connect AI-driven experiments to real performance metrics like CTR, CPA or incremental lift.
Types of generative AI used in marketing
Generative AI is not a single technology. It is a set of model types, each designed for different kinds of marketing content and workflows.

Knowing the differences helps marketers choose the right tool for each stage of a campaign.
Large Language Models (LLMs): LLMs generate text for ad copy, product descriptions, email subject lines and chatbot replies. They are especially valuable for A/B testing, since teams can create multiple variations and quickly see which improves CTR or lowers CPA. Tools such as ChatGPT, Jasper and Copy.ai are widely used, and they all excel at specific use cases. ChatGPT can generate first drafts of product descriptions at scale. Jasper is great for generating dozens of ad variations in minutes. Copy.ai can create multiple subject lines for A/B testing and help draft email campaigns.
Recent discussions of AI reasoning highlight how these models work in practice and what marketers should expect from them.
Diffusion models: These models create visuals like banners, product mockups and video frames. They allow creative testing before design resources are committed. Midjourney, Adobe Firefly and DALL·E are leading examples of tools that use this type of generative AI.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): GANs have been widely used for lifelike synthetic images and videos by pairing a generator with a discriminator. While less common in today’s mainstream creative tools, they still play a role in areas like creative testing, filling missing assets or generating 3D concepts.
Audio and speech models: These models create voiceovers, ad soundtracks and call scripts. Platforms such as ElevenLabs and Play.ht enable scalable personalization in audio and video campaigns.
Adoption in platforms: Meta’s Advantage+ automates targeting and creative combinations, assembling ad variants dynamically from your assets. Google Ads has introduced generative copy and imagery into its campaign builder. Both operate as black boxes, leaving marketers uncertain about what truly drives performance.
While platforms like Meta and Google are introducing generative features, their optimization engines remain predictive, not generative. The creative layer is GenAI; the delivery layer is AI optimization.
Funnel complements these black-box systems by validating which AI-generated creatives and channels drive incremental performance.
How generative AI supports key marketing functions
Generative AI is showing up across nearly every part of marketing, from content creation to measurement. For performance marketers, the value of AI is not just in producing more assets, but in testing them faster and grounding decisions in trustworthy data. Each function below highlights where AI tools are being applied today.
Content creation
Content creation is one of the clearest uses of generative AI in marketing. Instead of starting from a blank page, marketers can draft blog intros, newsletters and campaign copy in minutes.
Popular tools include:
- Jasper for fast blog and ad copy
- Writer for tone-controlled assets that align with brand guidelines
- ChatGPT for first passes of headlines, emails and campaign text
Beyond writing, generative AI tools create product descriptions and email drafts at scale. This saves marketing teams from repetitive tasks and lets them focus on strategy and more creative tasks.
They also make testing easier. A team can generate multiple landing page variants, run them in-market and see which version improves CTR, lowers CPA or drives stronger ROAS.
Generative AI in content creation is not about replacing marketers just yet. It is about producing more testable ideas, faster.
Social media campaigns
Generative AI is increasingly used to support high-volume social media campaigns. Marketers can create tailored post variations for each platform, produce captions in different tones and generate image options that are ready for rapid A/B testing. This makes it easier to manage both organic and paid activity across multiple channels.
Popular tools include:
- LatelyAI for repurposing long-form content into platform-ready social posts
- Canva’s AI tools for generating image variations and branded templates
- Ocoya for scheduling and producing captions across platforms
- Copy.ai for quick-turn caption and ad text suggestions
These AI tools let marketing teams plan campaigns faster and test more variations without extra design or writing resources. By running more experiments across Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn or TikTok, marketers can quickly see which formats lift engagement, improve CTR, lower CPA or lift ROAS.
Customer interactions
Generative AI is reshaping how marketing teams handle customer interactions. Chatbots manage FAQs, suggest products and respond in real time. These systems personalize replies by pulling from customer data, making them more useful than rule-based scripts. As a result, human support teams are freed up to focus on complex issues or high-value conversations.
Popular tools include:
- Drift for AI-powered chat that captures and qualifies leads
- Intercom Fin for customer service automation with conversational AI
- Ada for personalized chatbot experiences across multiple platforms
- HubSpot ChatSpot for combining CRM data with AI-generated responses
With these tools, customer queries are answered faster and more consistently. Performance marketers benefit because AI systems can highlight customer insights, uncover buying signals and direct traffic toward the campaigns or products most likely to convert.
Creative production
Creative production is where generative AI tools show their value most clearly. Instead of waiting days for design teams to produce options, marketers can spin up banner concepts, ad visuals or product mockups in minutes. That speed matters when campaigns depend on testing small differences that change performance.
Popular tools include:
- Midjourney for visual directions and banner mockups that spark early concepting
- DALL·E for creating product images or filling in missing variations for A/B tests
- Adobe Firefly for generating branded social assets that fit existing style guides
The immediate benefit is not perfect creative. It’s that you have more concepts to test. A lighter background, a different angle on a product or an alternate color palette can be trialed quickly. By knowing which variation earns more clicks or lowers CPA, teams can refine designs before investing in full production.
Generative AI speeds up testing, but scale only matters when you can measure what works. Later in this article, we’ll look at how AI and advanced measurement together turn experimentation into true performance gains.
Segmentation and personalization
Generative AI helps marketers go beyond broad audience buckets by grouping users based on demographics, behaviors or real-time interactions. Once you have user segments, you can deliver personalized recommendations, dynamic emails or tailored product suggestions that feel specific to each customer.
Popular tools include:
- Optimove for AI-driven audience segmentation and campaign orchestration
- Blueshift for personalization across email, mobile and web experiences
- Segment (Twilio) for collecting and activating customer data across channels
The benefit is practical: marketers can test whether a new audience split improves CTR or lowers CPA. By using both historical and real-time signals, teams can serve content that reflects what customers are likely to do next, not just who they were last quarter.
Unlike CDPs and personalization platforms, Funnel doesn’t store customer identities or orchestrate real-time targeting. Instead, it provides the independent measurement layer that validates whether personalization efforts are actually delivering incremental performance.
Market research
Generative AI also supports market research by analyzing unstructured sources like reviews, forums and customer feedback. These inputs reveal how people describe products in their own words, which helps marketers surface shifts in sentiment and identify new opportunities before they hit mainstream channels.
Popular tools include:
- Perplexity for summarizing emerging trends and answering customer queries with cited sources
- Claude for condensing competitor reports, blog posts and customer discussions into digestible insights
Instead of combing through thousands of comments, marketers can spot early signals and test campaigns around them. This shortens the gap between consumer conversations and actionable creative ideas.
Data insights and measurement
Generative AI is changing how marketers work with performance data at the campaign level. Instead of exporting spreadsheets or building manual reports, teams can ask conversational questions and get clear answers about which ads, creatives or audiences are moving the needle.
Generative AI makes it easy to spin up dozens of campaign variations or reports in minutes. But speed alone isn’t enough. Funnel ensures marketers act with control, clarity and confidence, so AI-driven campaigns are grounded in trustworthy data, not guesswork.
Without a reliable data foundation, generative AI risks amplifying noise. Funnel’s Data Hub solves this by unifying and harmonizing marketing data before anything gets created, tested or scaled. That’s how agencies like Publicis, Mediaschneider and Journey Further save thousands of hours each year and shift time toward strategy, not spreadsheets.
Funnel AI helps marketers go beyond dashboards. Teams can ask natural language questions about performance and get answers grounded in their unified data set. A marketer can ask, “Which campaigns reduced CPA last week?” and get an immediate, data-driven answer that separates real performance from noise.
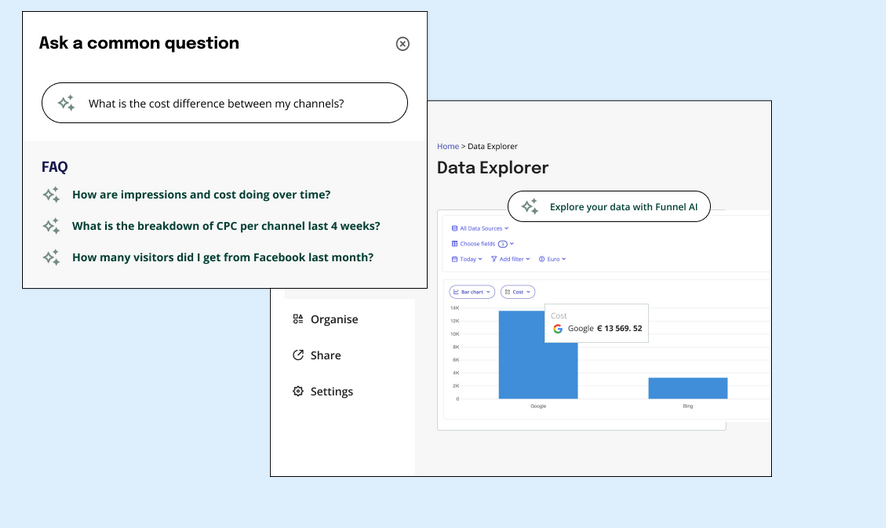
These types of fast insights can be game-changing. Instead of sifting through results data and connecting the dots, AI does it for you.
Control and compliance
Generative AI can speed up campaign production, but it also introduces risks if content drifts outside brand or legal boundaries. A single product claim written incorrectly or an image that fails accessibility standards can trigger compliance issues and damage trust. That is why marketers are adopting tools that put controls in place.
Popular tools include:
- Grammarly Business, which enforces tone and language rules across distributed teams
- Guardrails AI, which applies hard rules to generative outputs and blocks anything non-compliant
- Persado, which tailors language for regulated sectors like finance and healthcare
These systems give marketing teams confidence that AI-generated copy and visuals meet both brand and legal requirements before they go live. Speed is valuable, but only when paired with control.
AI + measurement
AI-generated assets only matter if they create incremental performance. That is where advanced measurement approaches like marketing mix modeling (MMM), multi-touch attribution (MTA) and incrementality testing come in. These methods validate whether new creative, channels or campaigns are actually driving lift or simply shifting conversions from one place to another.
Too often, teams test generative AI tools in silos. The real breakthrough happens when those experiments are connected with a marketing intelligence platform like Funnel. By unifying data, powering reporting and validating performance through advanced measurement, Funnel provides a complete foundation for AI-driven marketing.
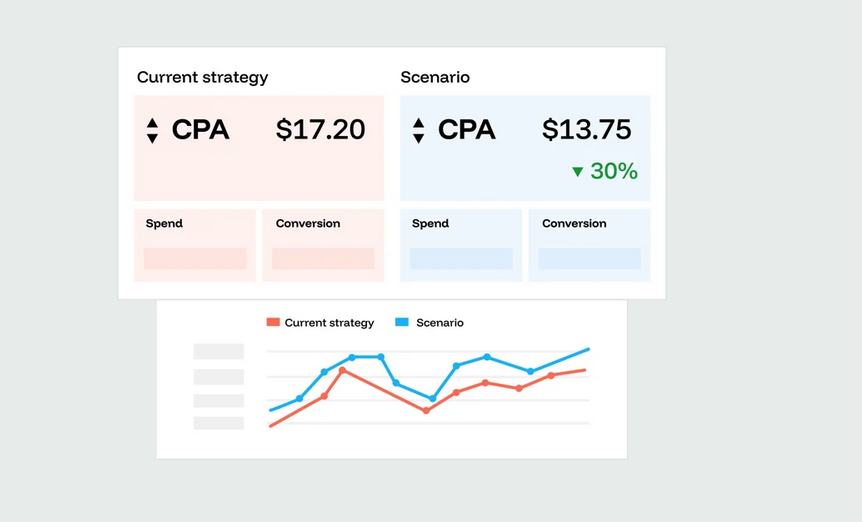
Funnel pulls data from hundreds of marketing channels and unifies it into our Data Hub, where it’s ready for analysis, reporting and measurement. Connections to marketing tools are fully managed, and data is continually refreshed. You can explore possibilities with built-in scenario planning and AI-assisted media optimization.
Funnel also supports conversion APIs. They send cleaner, server-side performance data back to platforms so their AI models optimize campaigns on real signals, not noisy or missing data. Funnel makes this easier by ensuring those signals are unified and trustworthy.
Challenges of generative AI in marketing and how to overcome them
Generative AI in marketing offers speed and scale, but it also introduces risks that can undermine campaign performance if left unchecked. Understanding these challenges and how to address them helps marketing teams capture the upside while avoiding common pitfalls.
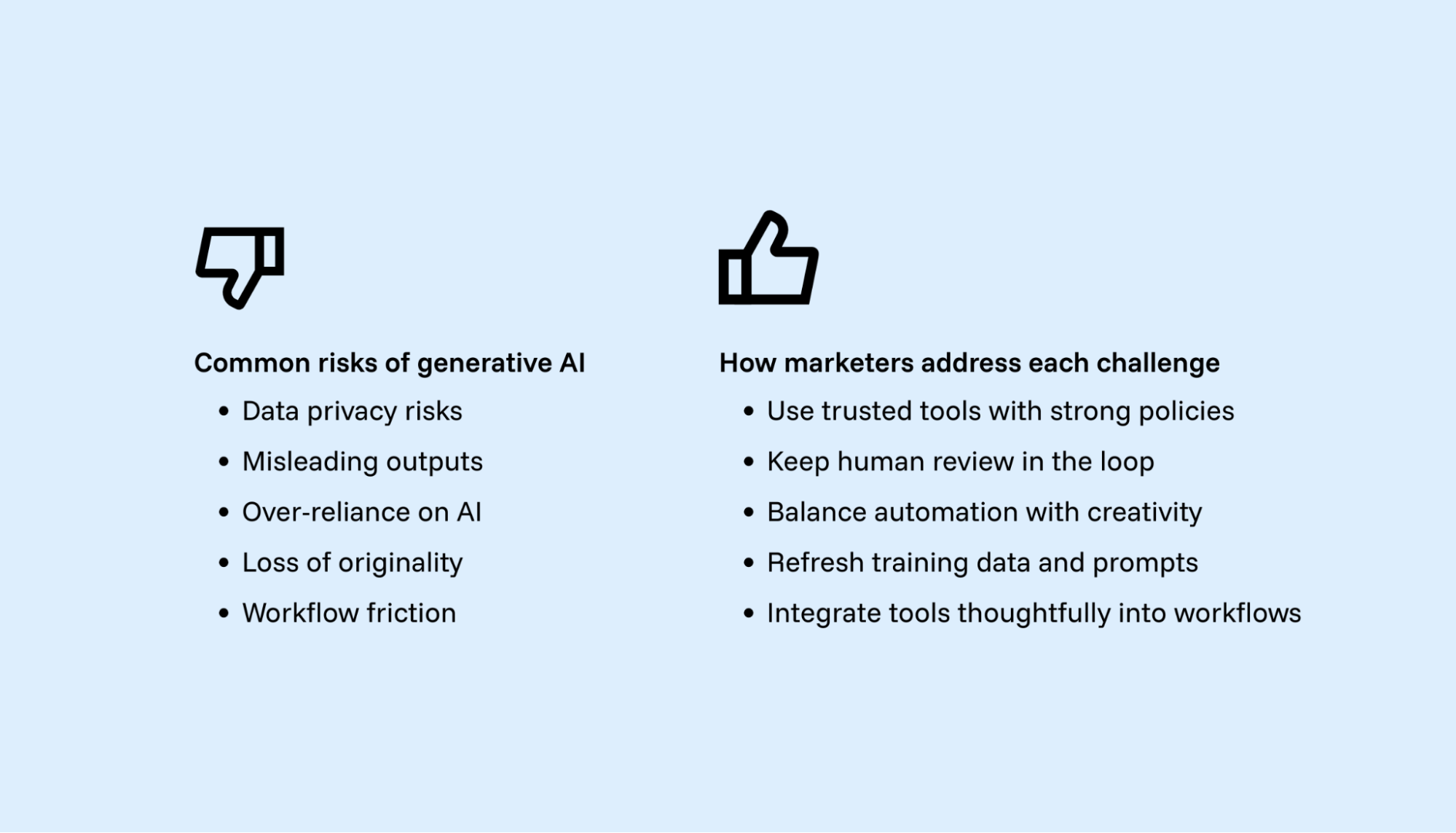
Data privacy risks. Mishandled customer data may violate GDPR or CCPA. Marketers should also be cautious about what they feed into generative AI systems. Avoid pasting customer PII or licensed creative into public tools. Instead, use enterprise solutions with governance controls or private model environments to ensure compliance with privacy and IP standards.
Misleading or incorrect outputs. Generative models sometimes hallucinate facts or misread customer sentiment. Keeping human review in the loop and cross-checking with verified data reduces this risk.
Over-reliance on AI systems. Automated outputs can miss cultural nuance or campaign context. AI should provide drafts and ideas, while marketers refine messaging to align with brand strategy.
Loss of originality. Repetitive prompts or shallow training data can lead to generic marketing content. Varying prompts and fine-tuning on brand-specific data helps maintain originality.
Integration friction. Most AI tools do not slot cleanly into marketing’s data workflow. Funnel bridges this gap by linking AI-driven content creation with unified, trustworthy data, making outputs measurable and actionable.
Bias amplification. AI systems can reinforce targeting or creative biases baked into training data. Marketers should audit outputs regularly and balance automated suggestions with human oversight to avoid skewed results.
The key to using generative AI in marketing is this: AI outputs are only as good as the data foundation. Without reliable integration and an independent layer, marketers risk scaling noise instead of performance. Funnel acts as the independent layer that validates AI outputs against unified, reliable data. It gives marketers not just more activity, but the clarity to know what’s working and the confidence to scale it.
What’s next for generative AI in marketing strategy?
The next wave of generative AI in marketing will be defined by how well tools create, personalize and adapt content at scale and how marketers measure which variations actually work.
Multi-modal generation. Instead of using separate tools for text, visuals and video, emerging models can create all three in one workflow. Marketers will be able to generate a complete campaign package with ad copy, product images and short-form video from a single prompt.
Personalization at scale. Generative AI tools are evolving to tune creative variations for micro-audiences in real time. Instead of running a handful of ad versions, you will be able to show each segment a version that reflects their preferences, browsing behavior or purchase patterns.
Brand-controlled fine-tuning. Teams are starting to train generative AI models on their own brand guidelines and historical campaign data. This keeps outputs consistent with tone and past learnings while reducing the risk of generic or off-brand content.
A more conversational, autonomous future. New tools like Sora and Atlas hint at where AI is heading — more conversational, more embedded and more autonomous. For marketers, that means faster answers and new ways to explore data. But speed alone isn’t enough. The next leap forward will come from combining these conversational interfaces with solid measurement frameworks, so every AI-generated recommendation is backed by trustworthy data. That’s the foundation Funnel provides.
Looking ahead to general intelligence. The conversation around AI is expanding beyond generative tools toward general intelligence, systems capable of reasoning and adapting far beyond today’s models. While it’s too early to know exactly how AGI will shape marketing, one thing is certain: it will make trust and measurement even more critical. As AI systems become more autonomous, marketers will need independent validation layers like Funnel to ensure that insights and optimizations are grounded in reality, not algorithmic assumptions.
Generative AI can flood campaigns with endless variations, but volume alone doesn’t guarantee performance. Funnel provides the independent measurement layer that validates which creative versions and channels deliver incremental results. And with Funnel Activate, those insights don’t just sit in reports — they flow back into ad platforms as clean, privacy-safe conversion signals. This helps platforms optimize targeting and bidding more accurately, so marketers can scale what works with confidence.
How Funnel helps performance marketers use AI
Instead of relying on black-box platforms, Funnel acts as the independent layer marketers can trust. It’s not just measurement — it’s control. Funnel combines data integration, reporting, measurement and activation in one platform. That means you can unify and analyze data, validate performance, and send accurate conversion signals back to ad platforms, BI tools or warehouses to optimize spend when needed.
Funnel AI supports this by enabling conversational analytics and daily-updated MMM and attribution models. Together, they give marketers a clearer view of performance and the confidence to reallocate budgets based on evidence, not assumptions.
If you’ve outgrown templates and static dashboards, Funnel helps you turn complex marketing data into clear, actionable insights that prove impact and drive growth.
FAQs on generative AI in marketing
Generative AI is changing how marketing teams work, but it also creates questions about where it fits best. Here are answers to some of the most common ones.
How does generative AI improve content creation and customer engagement?
It reduces the grunt work of drafting. A team launching 200 new SKUs can use AI to generate product descriptions in hours instead of weeks. Marketers then edit for tone and accuracy rather than starting from scratch. On the engagement side, generative AI adapts copy and visuals based on customer data. For example, social media captions can change depending on user preferences, or an email subject line can reference a recent purchase.
What are the top generative AI tools for marketing teams?
Marketers today rely on a mix of general-purpose and specialized AI tools, depending on the task.
- For writing and ideation: ChatGPT, Gemini and Claude handle ad copy, email variations and campaign concepts with advanced context control. (Some teams still use niche tools like Jasper or Writer for brand-specific templates.)
- For visuals: Midjourney, Adobe Firefly and DALL·E generate ad banners, mockups and social assets.
- For research and summarization: assistants such as ChatGPT, Claude and Perplexity make competitive analysis and planning faster.
Can generative AI help with SEO and customer insights?
Yes, AI can propose keywords, headings and meta descriptions that improve search rankings. It can also scan unstructured data like customer reviews and support logs to flag recurring pain points. This gives marketers faster insight into what customers actually say and how campaigns should respond.
Which industries are adopting generative AI technologies fastest?
Retail and ecommerce use it for bulk product content, media companies for scaling creative variations, and SaaS businesses for personalized outreach across email and chat.
How are marketers using LLMs to improve content and ad copy?
Large language models draft variations of web pages, product descriptions and email subject lines. Teams review for tone, brand fit and factual accuracy. Some also use LLMs to spot jargon or suggest alternatives, making edits more efficient.
How do marketers measure the ROI of generative AI in marketing?
They look at efficiency (time saved on drafts and approvals), creative impact (CTR, open rates, conversions) and testing velocity (more A/B tests run in less time). Funnel adds value by showing whether AI-generated content drives incremental lift instead of just producing more output.
How does AI change the role of marketers?
Automation has already changed the marketer’s day-to-day by removing repetitive work by collecting, normalizing and distributing data across dashboards. Funnel does this at scale so teams can spend less time chasing spreadsheets and more time interpreting results.
AI takes that shift further. Instead of just streamlining tasks, it helps marketers make smarter decisions. In Funnel Measurement, advanced statistical models and machine learning analyze performance data to show what’s really driving results and where to allocate spend next.
Together, automation and AI free marketers from manual reporting and move their focus toward strategy, experimentation and creative testing.
Can generative AI replace measurement?
No. Generative AI can help create content, and optimization algorithms can distribute it, but measurement is what proves impact. Funnel’s measurement suite uses advanced machine learning models across marketing mix modeling (MMM), multi-touch attribution (MTA), and incrementality testing.
These AI-powered models run daily, automatically reconciling insights across methods to show what’s truly driving results. That independent validation turns AI-driven experimentation into accountable, data-backed growth.
-
Written by Christopher Van Mossevelde
Head of Content at Funnel, Chris has 20+ years of experience in marketing and communications.
